Phishing – in its many varieties – is the threat security leaders in the legal sector are most concerned about. Why? Because attacks are frequent, hard-to-spot and, when successful, have various serious consequences, including loss of client trust, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
In this blog, we will explore what spear phishing is, the characteristics of a suspicious email, and what security methods you should put in place to protect your data and legal practice from being breached.
What is spear phishing?
Spear phishing, much like ‘regular’ phishing, is a kind of social engineering cyberattack, during which, a cybercriminal pretends to be a legitimate, reliable figure in order to mislead somebody into passing on confidential information, revealing their credentials, or installing malware onto their device.
While both phishing and spear phishing share characteristics, such as being delivered by email, using coercive language and depending on impersonation, there are several distinctions that will allow you to differentiate between the two.
The latter targets a single individual or a small group of people, such as your Finance Team. The message is highly personal and includes information and tactics that make the email believable to the recipient. And finally, zero-payload attacks are common – attacks that exploit a vulnerability that is either unknown or known and without a patch to correct it.
Spear phishing email example
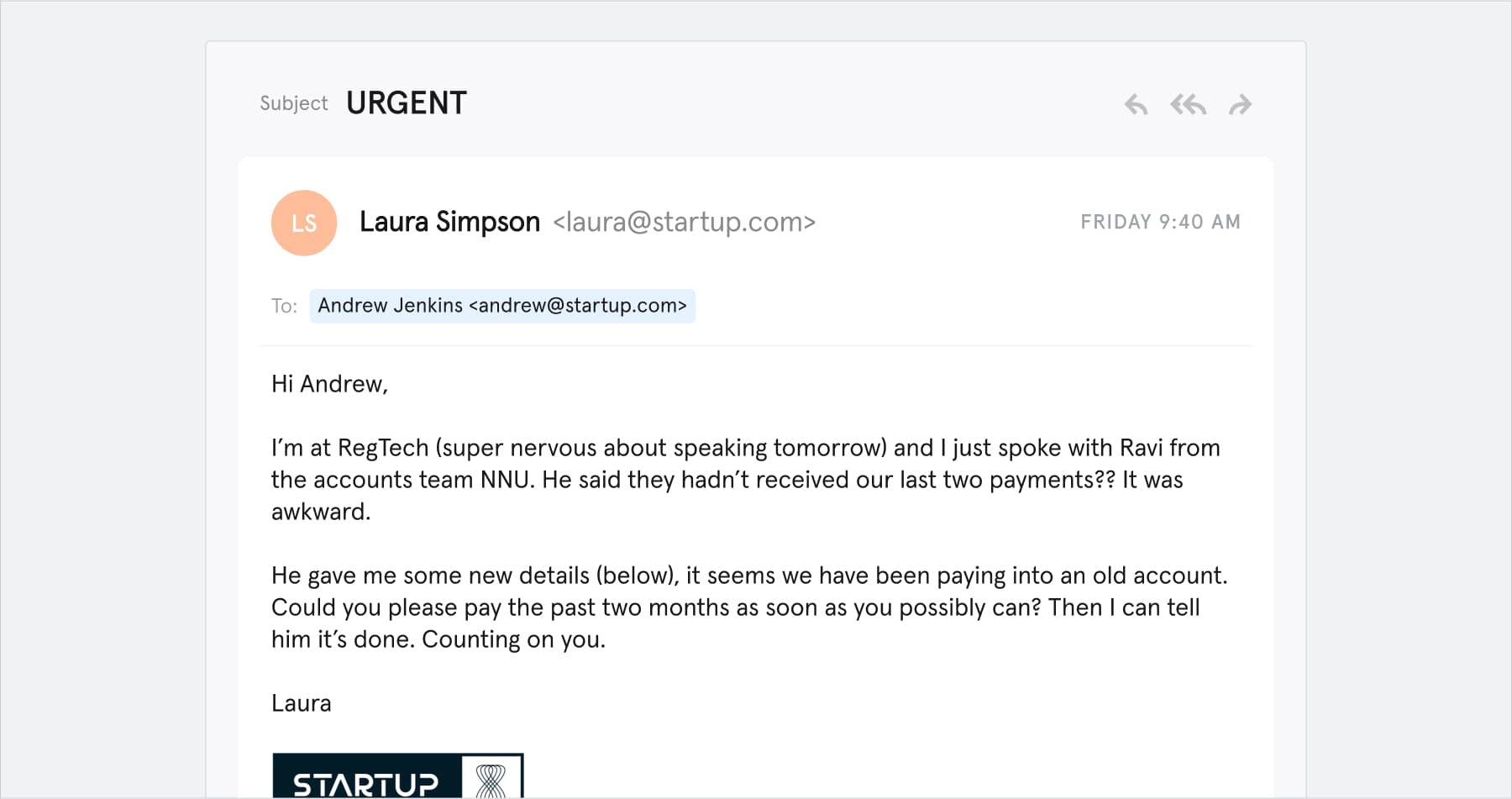
The key characteristics
- The sender’s email address is real; therefore, the email isn’t noticeably suspicious. Email spoofing or account takeover are methods hackers use to appear genuine, fooling the recipient to possibly disclose sensitive information.
- The hacker has included authentic, personal information, which can be mined from the recipient’s social media accounts.
- There is a sense of urgency to the message, which takes advantage of human psychology – the sender aims to exploit the target’s trust, placing them under pressure, which can often lead to bad decisions being made.
Taking a layered approach to security
- M365 security
M365 has built-in security measures that span user access, threat protection and information storage. The level of control that Microsoft provides its users gives you the ability to apply access permissions to emails, data access via SharePoint or OneDrive, and the ability to centralise policy and governance.
- Email security
Legacy email security controls rely on rule-based methods of threat detection and are unable to prevent security threats caused by people. Attackers evolve their techniques; email networks are dynamic in nature and human behaviour is inconsistent and unpredictable meaning rules are out of date as soon as they are created, and signature-based approaches are completely ineffective.
To prevent today’s advanced email security threats, your security controls must have the ability to continually analyse, adapt and evolve based on an understanding of normal and irregular human behaviour.
- End-user training
Cybersecurity is the responsibility of everybody within your firm or chambers, not just your IT department. There is an undeniable link between basic cybersecurity knowledge and the mitigation of breaches – it is vital that your end users undergo continuous training to keep abreast of the ever-evolving threat landscape.
The legal world is built on reputation. CTS’ Cyber Protection service supports the legal sector to manage and protect its data at every stage of the security lifecycle. Contact CTS today to enquire about how we can assist your firm with a technology health assessment.




